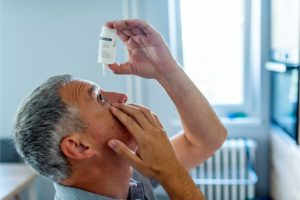
The most common treatment for glaucoma is prescription eye drops. While they won’t cure the disease or reverse vision loss, eye drops for glaucoma help by lowering the pressure inside the eye (intraocular pressure) to reduce the risk of damage to the optic nerve.
It is important to inform your eye doctor about any other medications you may be taking, including over-the-counter items like vitamins, aspirin, and herbal supplements, and any allergies you may have. Some types of prescription eye drops for glaucoma may not be suitable for patients with certain health conditions or who are taking certain medications.
Some common side effects of glaucoma treatment eye drops include stinging or burning in the eyes, redness, headaches, and blurred vision. These symptoms may improve over time, but if you experience any severe or persistent side effects, you should contact your eye doctor right away.
To minimize the risk of side effects, it is recommended to decrease the amount of glaucoma eye drops that can be absorbed into the bloodstream. This can be achieved by closing the eye and pressing on the inner corner of the eye near the nose for a few minutes after applying the eye drop. This technique increases the amount of drug absorbed by the eye and reduces the amount that passes through the tear ducts.
Glaucoma eye drops are typically used once or twice a day, sometimes up to four times a day, and they must be used consistently in order to be effective. It’s important to follow the instructions provided by your doctor or pharmacist for how to use the eye drops properly.
In addition to using your glaucoma eye drops as prescribed by your ophthalmologist, regular eye exams and ongoing communication with your glaucoma specialist are essential for maintaining good eye health and preventing vision loss. For more information on glaucoma treatment options, including laser surgery, schedule an appointment at Washington Eye Physicians and Surgeons.
© 2025 Washington Eye Physicians & Surgeons
The material contained on this site is for informational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health care provider.